Was ist ERP Software?
ERP Software besteht im Kern aus einer zentralen Datenbank mit allen relevanten Unternehmensdaten und kann so als Instrument der Planung, Steuerung und Kontrolle genutzt werden. Die Abkürzung ERP steht übrigens für “Enterprise Resource Planning” und bezeichnet im eigentlichen Sinne “die unternehmerische Aufgabe, Ressourcen wie Kapital, Personal, Betriebsmittel, Material und Informations- und Kommunikationstechnik im Sinne des Unternehmenszwecks rechtzeitig und bedarfsgerecht zu planen, steuern und verwalten” (siehe Wikipedia: Enterprise-Resource-Planning).
Was ist ein ERP System? Die Für-Jedermann-Erklärung in 80 Sekunden:
Wie funktioniert ein ERP System?
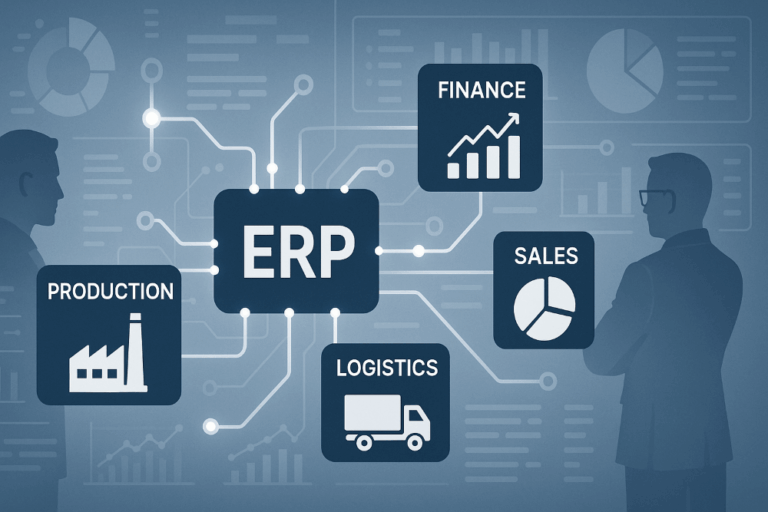
ERP Systeme bestehen aus unterschiedlichen Modulen für die einzelnen Unternehmensbereiche. Durch die Auswahl der relevanten Module wird die ERP Lösung an Unternehmen aus den unterschiedlichsten Branchen und für die jeweilige Unternehmensgröße angepasst.
So kann dieselbe Software sowohl bei einem Dienstleister mit 10 Mitarbeitern, einem Handelsunternehmen mit 100 Mitarbeitern und auch einem Fertigungsbetrieb mit 1.000 Mitarbeitern erfolgreich eingesetzt werden. Die Produkte der großen ERP Anbieter sind in nahezu allen Branchen einsetzbar, wobei die kleineren ERP Anbieter oftmals einen Fokus auf bestimmte Branchen haben.

Das Basispaket von ERP Systemen kann aus folgenden Modulen bestehen (abhängig vom jeweiligen ERP Software Hersteller):
- Finanzen
- Beschaffung
- Materialwesen
- Produktion
- Vertrieb
- Logistik
Und folgende Erweiterungsmodule können zur Verfügung stehen (abhängig vom jeweiligen ERP Software Hersteller):
- Projektwesen
- Service
- Dokumentenmanagement (DMS)
- Marketing / Kundenbeziehungsmanagement (CRM)


Ein weiterer Erfolgsfaktor von ERP Systemen ist die Integration mit anderen Softwareprodukten (abhängig vom jeweiligen ERP Anbieter):
- Office Software (z.B. Microsoft Excel, Word, Outlook)
- Reporting Tools
- Business Intelligence (BI)
- Elektronischer Datenaustausch mit Lieferanten, Kunden und Partnern (EDI)
- E-Commerce
Einige ERP Anbieter bieten Spezialmodule für bestimmte Branchen mit besonderen Anforderungen an, so z.B. für die Bereiche Pharma, Verlage, Bau, IT, Behörden und Versicherungen.
Dieser modulare Aufbau von ERP Lösungen gibt dem Kunden die Möglichkeit, die Software in mehreren Phasen einzuführen und auf künftige Veränderungen flexibel zu reagieren. In einem idealen Szenario wächst die ERP Software mit den Anforderungen des Unternehmens mit. Das ist eine der grundsätzlichen Ideen und großen Vorteile von ERP Systemen.
Doch nicht mit jedem ERP Anbieter wird das so reibungslos funktionieren. Und auch wenn es funktioniert steht es nicht automatisch im gewünschten Kosten-/Nutzenverhältnis. Deswegen ist die Auswahl der optimalen ERP Software von entscheidender Bedeutung, insbesondere mit künftigen Anforderungen im Hinterkopf.
ERP System Beispiele
ERP System Beispiele findet ihr in unserem Vergleich der wichtigsten ERP Anbieter. Diese aktuelle Marktübersicht der ERP Anbieter zeigt euch, welche Anbieter sich für kleine Unternehmen, für den Mittelstand und für große Unternehmen eignen.
Ein anschauliches Beispiel aus der Praxis: Erfahrt in zwei Minuten, wie ein Cloud ERP System die Integration unterschiedlicher Warenwirtschaftssysteme und Standorte ermöglicht:
Top 5 ERP Systeme
Ermitteln Sie die Top 5 ERP Systeme für Ihr Unternehmen punktgenau aus 700+ Anbietern – kostenlos und unverbindlich.

Rund 500 Unternehmen nutzen unsere effizienten Services und Tools bei ihrer ERP Software Auswahl – jedes Jahr.